How Packaging Plays a Key Role in Food Safety Compliance
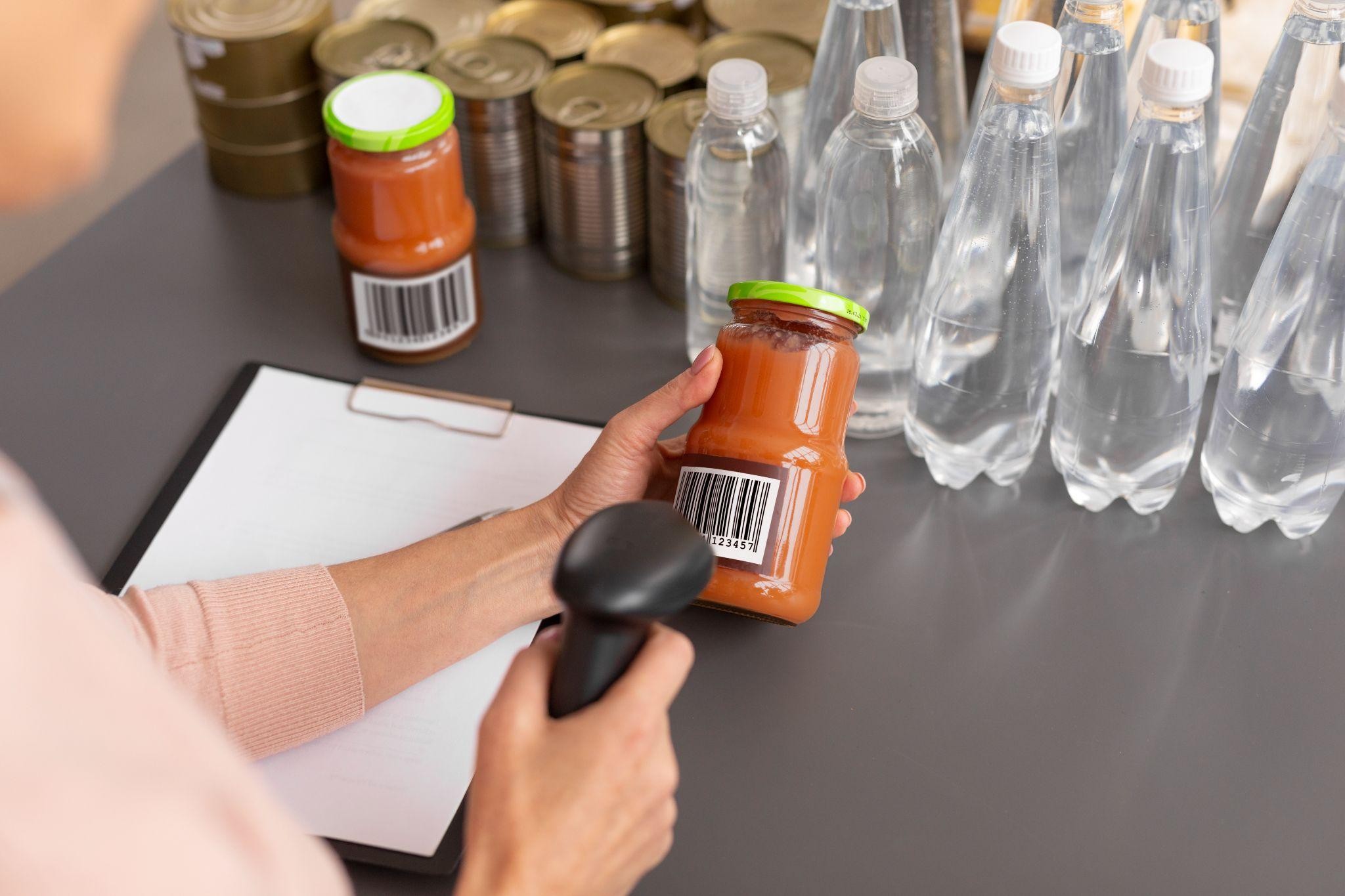

One of the biggest challenges in the food industry is ensuring that products remain safe from contamination throughout their journey to consumers. Contamination, whether microbial, chemical, or physical, can lead to foodborne illnesses, putting public health and a brand’s reputation at risk.
The solution to this problem lies in effective packaging. Proper packaging not only safeguards food from external threats but also ensures compliance with strict food safety standards. In this article, we’ll explore how packaging plays a critical role in food safety compliance providing a reliable solution to these pressing issues.
Packaging Standards and Regulations
Food packaging must comply with strict global regulations to ensure that products are safe for consumption. These standards help minimize the risk of contamination and maintain food quality. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration): FDA ensures packaging materials are safe for food contact and prevents contamination from harmful substances.
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points): HACCP focuses on identifying potential hazards in food production and packaging, ensuring food safety at every stage.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO provides guidelines for packaging materials, ensuring they meet safety, quality, and environmental criteria.
The materials used for food packaging, whether plastics, metals, or paper, must meet these regulations to prevent contamination and extend shelf life. Adhering to these packaging standards is crucial for maintaining food safety and consumer confidence.
Types of Packaging That Ensure Food Safety
Different types of food packaging play a crucial role in ensuring food safety. Each type offers unique benefits to prevent contamination and extend shelf life:
Airtight Packaging
This packaging type seals food tightly, preventing moisture and air exposure, which helps keep food fresh and prevents spoilage, especially for perishable items like meats and baked goods.
Barrier Packaging
Designed to protect food from external contaminants, such as dust, bacteria, and UV rays, barrier packaging ensures that food maintains its quality and flavor for a longer period by blocking harmful elements.
Tamper-Evident Packaging:
This type of packaging provides visible signs if a product has been tampered with, offering consumers peace of mind that the product is safe to consume. It is commonly used for pharmaceuticals and ready-to-eat meals.
Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Packaging
Made from renewable materials, this packaging option not only meets safety standards but also supports environmental sustainability by reducing plastic waste, making it an ideal choice for eco-conscious consumers.
Food Packaging Innovations and Trends
Food packaging innovations are continuously evolving to enhance food safety and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Vacuum sealing: By removing air from packaging, vacuum sealing prevents spoilage and reduces the growth of harmful bacteria, keeping food fresher for longer periods.
- Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP): This technique alters the gases inside the packaging to slow down food deterioration, helping to preserve the freshness of perishable items like fruits, vegetables, and meats.
- Active packaging: This type of packaging incorporates elements such as moisture absorbers or oxygen scavengers that interact with the food to maintain quality, reduce spoilage, and extend shelf life.
These advancements play a key role in extending shelf life, maintaining product quality, and preventing contamination:
Endnote
Food safety compliance plays a crucial role in the food industry, and packaging ensures it. Businesses must prioritize effective packaging solutions as consumer expectations increase and regulations become stricter. By following safety standards and adopting new innovations, companies can maintain food safety and meet regulatory requirements. The future of food safety practices will be shaped by advancements in packaging technology.